- For Orders 98413 88259, 98404 19420, 98407 41420
- sales@msvwatertech.com, projects@msvwatertech.com
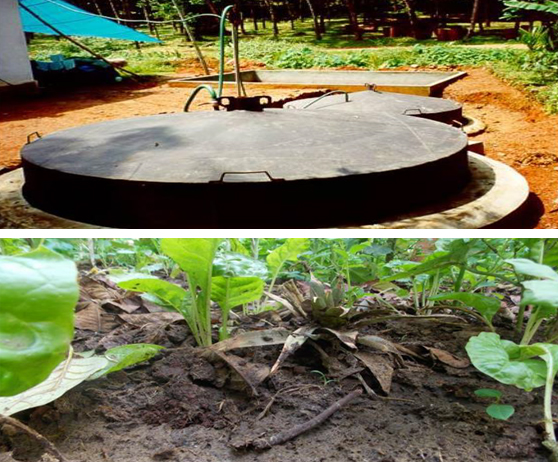
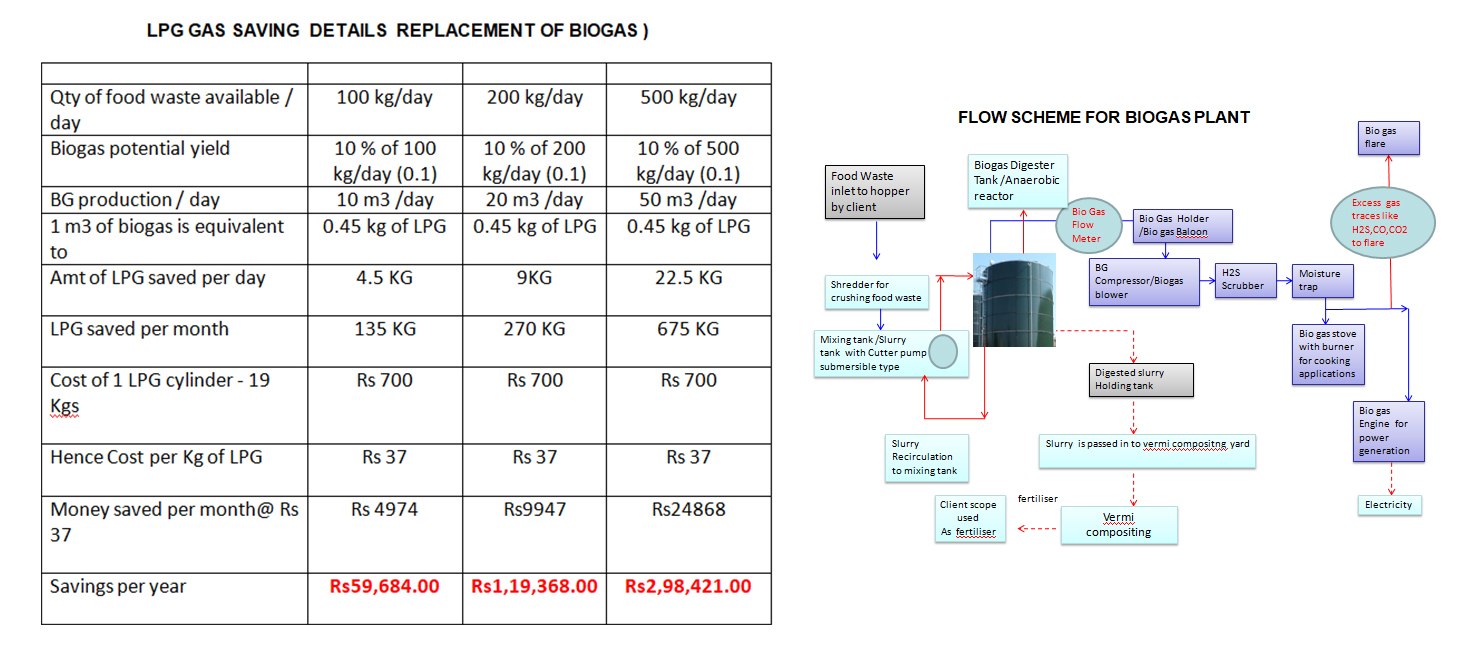
Biogas is a colour less ,odourless ,inflammable gas produced by organic &bio mass decomposition (fermentation)
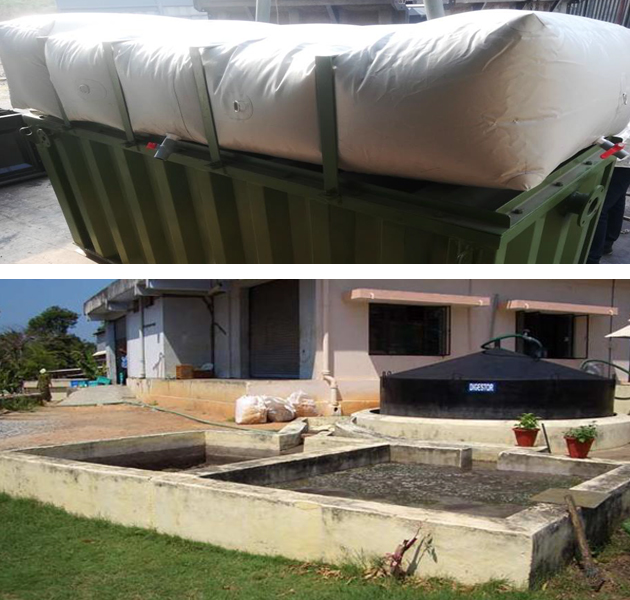
The anaerobic digester system for anaerobic digestion of biodegradable waste is provided for biogas production and recovery. The anaerobic digester system includes substantially fixed horizontal digester for digesting the waste with biogas production and transmitting the biogas to a biogas storage balloon overhead. In the anaerobic digestion process, microorganisms participate in a web of interacting processes which result in the decomposition of complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins to the final products of the methane and carbon dioxide.
The anaerobic digestion process can be divided into three main steps.
In the first step hydrolysis, microorganisms aided by enzymes, decompose the complex organic compounds to simpler compounds such as sugar and amino acids. A number of intermediate products are formed in the next step (fermentation), including alcohols, fatty acids and hydrogen gas.
Methane is formed in the last step by a unique group of microorganisms (methanogens) that have very specific environmental requirements. Methanogens grow slowly and die if they come into contact with oxygen.
They also need access to certain vitamins and trace elements and are sensitive to rapid changes in temperature, acidity (pH) and other environmental factors. In starting and running a biogas process, it is very important to be aware of the nature of the biological processes involved, and to adapt the technology to meet the environmental and nutritional requirements of the microorganisms.

A variety of factors affect the rate of digestion and biogas production. The most important istemperature. Biogas production is carried out at different temperatures: temperature range 45–60 °C is referred to as ‘thermophilic,’ whereas that carried out at temperature range 20–45 °Cis known as ‘mesophilic’ and at low temperatures (<20 °C) is referred to as). The temperature below their optimum for growth microorganisms are unable to attach substrates from their environment because of lowered